If you’re like me, you want to put only the highest-quality products into your body.…
TOC
What Is Protein? Top Benefits And Usage.

02/18/2020 · 11 min reading
If there is one thing I recommend to all my clients, it’s protein! Whether they are athletes or casual gymgoers, protein benefits everyone.
Protein has so many critical roles in your body, especially for muscle growth. Protein has benefits for bodybuilders, runners, yoga practices, and everything between.
I supplement with protein powder and focus on dietary protein religiously. I have never gotten anything but good results from my clients and my own exercise regimen!
Smaller building blocks called amino acids 8 create proteins. Different combinations of 20 amino acids pair up to make different types of protein. 9 of these amino acids are “essential.” In this case, essential means that you must get them through food. Your body cannot make these amino acids on its own.
Complete proteins contain all 9 essential amino acids. The names of these amino acids are:
- Histidine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Lysine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Valine
Protein is also 1 of the 3 macronutrients 3. These macronutrients consist of protein, fat, and carbs. These are the core nutrients that your body requires for it to function. Your body doesn’t keep a backup store of this vital nutrient, so you have to continuously consume it.
What Does Protein Do?
Protein has countless benefits and functions 12 within your body. Some of the significant roles of protein are:
- Supports cell repair and the production of new cells
- Helps your immune system fight off infections
- Helps with body growth and development throughout your whole life
- Produces hormones and enzymes
- Vital to muscle growth and toning

Appetite Reduction
Consuming plenty of protein keeps you fuller 13 for longer times. Protein lowers hormones that cause hunger and boosts hormones that signal fullness.
Increasing protein intake by 15-30% leads to reduced intake by about 441 calories. This benefit was achieved without purposely restricting calories. If you’re looking to lose weight, lowering carbs and fats and upping protein can help you.

Muscle Growth and Strength
Without protein, your muscles cannot grow properly. Athletes maintain protein-rich diets to bulk up their muscle mass and strength performance. Additionally, your muscles strengthen to benefit any gymgoers and any exercise regimen. This happens even when losing weight from fat accumulation.
Bone Health
Contrary to popular belief, long-term protein intake is proven to support bone health. Adequate protein consumption reduces the risks of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis would otherwise put you at increased risk for broken bones. Women are more prone to osteoporosis after menopause, so it is extra important!
Keeps Your Cravings Under Control
Cravings become habitual due to your brain craving a rewarding feeling. This differs from regular hunger, which is a normal signal that your body needs nutrients.
Increasing your protein intake can lower your cravings by around 60%. Appetite control also works toward reducing your cravings.

Increased Energy
Without enough protein, your body uses the protein that your body needs 6to function. In this case, your body breaks down your necessary proteins into amino acids. This is for your body to use the amino acids to create glucose for energy.
With plenty of protein, your body functions and has extra. The extra protein provides energy and builds muscles!
Metabolism and Burning Fat
The thermic effect of food (TEF) is what changes your metabolism. During digestion, calories are burned for efficiency while breaking down nutrients. TEF is different for different types of food. Higher TEF increases the number of calories you burn during digestion.
Protein increases your metabolism 11 by having a higher TEF than fat and carbs. The TEF of carbs and fats is around 5-15%, while protein is 20-35%. Studies show that high-protein diets can burn up to 260 calories during digestion.
Control Blood Pressure
A wide range of health risks come with high blood pressure. These risks include strokes and heart attacks or heart diseases. Eating more protein can decrease blood pressure levels 1 as well as bad cholesterol 4.

Weight Loss Maintenance
With most diets, weight loss occurs while actively dieting. Unfortunately, once the diet stops, the pounds come right back.
As I mentioned, protein lowers calorie intake, boosts your metabolism, and reduces cravings. This quickly leads to weight loss. If you maintain a high-protein diet, the pounds will shed and stay gone 19.
Body and Tissue Repairs
Since protein is your building block, extra nutrition in your cells assist recovery. Protein is also proven to reduce muscle damage during exercise.
This also applies to other body injuries. Your skin and organ tissues build back up sooner to promote a shortened recovery period.
Prevents Muscle Weakness From Aging
Muscles begin deteriorating as we age. This can significantly reduce your quality of life and functioning during day-to-day activities.
Pairing a protein-rich diet with strength training can prevent age-related deterioration 17.

Stronger Immune and Nervous Systems
Proteins make up the antibodies that your body produces to fight infections. These antibodies detect infections and begin eliminating them to protect your body. A diet rich in protein allows your body to create antibodies more efficiently.
Your nervous system 16 also relies on protein. Your body sends signals to your brain, and your brain sends out the proper response. Protein supports your nervous system by improving the reception and transmission of signals.
Hair and Skin
Your body requires protein to build skin and replace dead skin. Many beauty products emphasize the role of collagen for healthy skin. They are undoubtedly right about the vital part that collagen plays.
Collagen itself is a form of protein. Increased protein allows your body to produce more collagen 16 that promotes skin health.
Protein also plays a crucial role in hair growth, health, and damage prevention.

Types of Protein Powder
One of the most common protein supplements is protein powder. There are several types of powders that 2 are beneficial in different ways.
Whey
Most people turn to whey protein to mix and make protein drinks.
Whey protein 10 comes from milk by separating milk curds from the protein. Your body quickly absorbs whey, and whey powder is a high-quality protein supplement. Whey is generally more effective in concentrated amounts than other powders. It is especially useful for post-workout shakes.
Casein
Casein powder has high amounts of an amino acid called glutamine. This amino acid is excellent for muscle recovery. It delivers nutrients throughout your day or night.
Soy
Soy protein is one of the complete proteins, containing all 9 essential amino acids. Since whey comes from milk, soy is an ideal alternative for vegans or lactose intolerance.
Pea
Another option if you are avoiding animal products is pea protein. This is another complete protein, much like soy. Besides the 9 essential amino acids, pea protein is also rich in arginine. Your body requires arginine for building muscle.
Egg
Egg protein is yet another animal-free option. This protein is high in the amino acid lysine. Lysine 9 promotes collagen growth, supports your immune system, and produces hormones.
Hemp
Hemp is perfect for anyone allergic to dairy or completely vegan. Hemp protein is entirely plant-based. Of the few plant-based proteins, even less are complete proteins like hemp. This protein is full of vitamins, minerals, and enzymes. It assists your body with absorbing and digesting, as well as general body health.
If you aren’t a fan of protein drinks or shakes, there are recipes for snacks that you can make using your powder!

How to Take Protein
How much protein you take and when you take it provides different benefits.
Dosage
Deciding your daily protein intake is simple. If you prefer, there are protein calculators 15 available. These calculators use many factors to determine your unique needs. These factors include:
- Whether you are male or female
- Age
- Height
- Weight
- Activity level
For calculating your requirements yourself 7, there is a general rule of thumb. For metric measurements, you should get around 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight. In imperial measurements, this adds up to about 7 grams of protein per 20 lbs of body weight. If you live a highly active lifestyle or aim for muscle gain, you can increase this amount 12. This can range from 1.0-2.2 grams per kilogram. In lbs, that makes 0.45-1 grams per pound of weight.
Protein should make up 10-35% of your daily calories. You can split up your daily amount in many meals, snacks, or shakes.

Timing
Although protein is beneficial at any time of day, some timing can work better 2].
Supplementing with protein at breakfast can set the stage for the rest of your day. After a full night of sleep, your body needs the rich nutrients that protein provides. You can also add powders to pancake mix or other breakfast items.
Taking protein around 30 minutes before a workout can reduce muscle damage. Adding simple carbs such as fruit to your protein gives you a bonus energy boost.
For recovery, the best time to take protein is right after your workout. Protein is vital to repairing muscle damage and building new muscle tissue.
Good Protein Sources
Protein supplements are helpful, but you should include high protein foods. There are many protein sources to choose from.
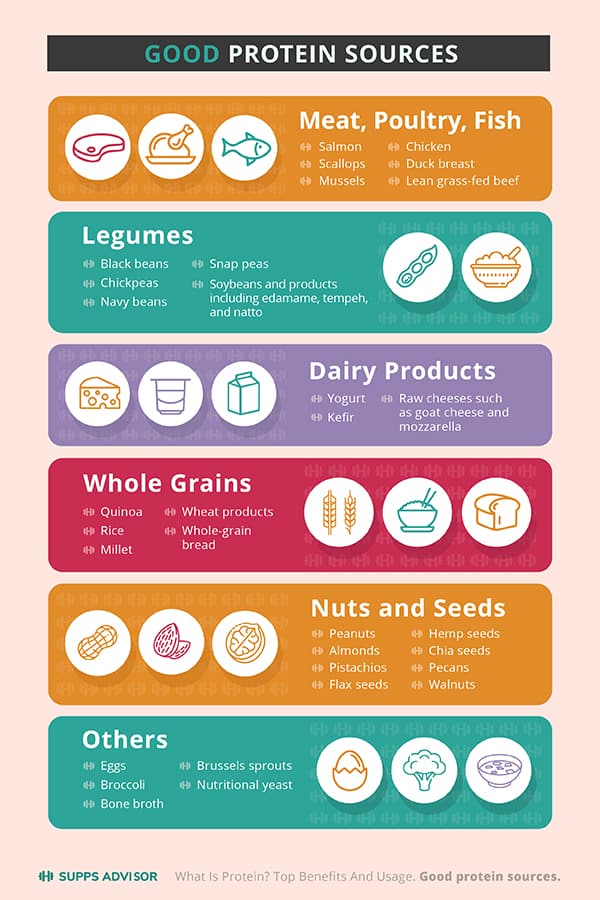
Meat, Poultry, Fish
Meat, fish, and poultry are some of the best protein sources. Even though all meats contain protein, not all of them are all-around healthy. Lean meat is preferable to avoid saturated fat and sodium 7. Ideal meat choices include:
- Salmon
- Scallops
- Mussels
- Chicken
- Duck breast
- Lean grass-fed beef
Great source for all-natural, grass-fed and pasture raised meats 18
Legumes
Other high protein foods 5 include beans and lentils. Here are some excellent examples:
- Black beans
- Soybeans and products including edamame, tempeh, and natto
- Chickpeas
- Navy beans
- Snap peas

Dairy Products
- Yogurt
- Kefir
- Raw cheeses such as goat cheese and mozzarella
Whole Grains
- Quinoa
- Rice
- Millet
- Wheat products
- Whole-grain bread

Nuts and Seeds
- Peanuts
- Almonds
- Pistachios
- Flax seeds
- Hemp seeds
- Chia seeds
- Pecans
- Walnuts
Others
- Eggs
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Bone broth
- Nutritional yeast
Possible Side Effects of Protein
Despite the amazing benefits of protein, it is possible to overdo it. This can lead to unpleasant risks and complications 16.
Neglecting Other Nutrients
If you focus too much on protein, you may miss out on your other necessary nutrients. Tracking your calorie and nutrient intake is important to maintain a balanced diet.
Weight Gain
Although protein is useful for weight loss, overdoing it can have the opposite effect. If you take in too many calories, your weight loss efforts will fail. An overabundance of amino acids can turn into fatty acids and pack on the pounds. If you aren’t looking to bulk your muscles, don’t devote a too high percentage of calories to protein.
Aggravating Existing Conditions
If you have medical conditions such as kidney or heart diseases, be careful with your protein intake. Excess protein puts stress on your kidneys to eliminate the waste. If you overeat animal-based protein, you risk raising your cholesterol levels.
Bone Loss
In ideal amounts, protein helps your bones. Your body eliminates calcium through urination when there is excess protein. Calcium is essential for bone health, so your protein intake needs to balance with calcium intake.
Protein offers so many benefits for health and fitness! Everyone can benefit from a balanced, protein-rich diet. Make sure that you include all other necessary nutrients by tracking your calories. Whether you use food or powder, many perfect choices are available for every person’s needs!
References
- Altorf-van der Kuil, W., Engberink, M., Brink, E., van Baak, M., Bakker, S., & Navis, G. et al. (2010). Dietary protein and blood pressure: a systematic review. Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Anderson, T. (2014). What are the benefits of protein powder, and should you take it?. Cosmopolitan.
- Anti, R. (2020). Macronutrients 101: Understanding the Basics – Aaptiv. Aaptiv.
- Appel, L., Sacks, F., & Carey, V. (2005). Effects of Protein, Monounsaturated Fat, and Carbohydrate Intake on Blood Pressure and Serum Lipids. Jama Network.
- Axe, D. (2019). Top 23 High-Protein Foods to Eat (for Weight Loss and Muscle Gain). Dr. Axe.
- Bray, G., Redman, L., de Jonge, L., Covington, J., Rood, J., & Brock, C. et al. (2015). Effect of protein overfeeding on energy expenditure measured in a metabolic chamber. – PubMed – NCBI. Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- College, H. (2020). Protein. The Nutrition Source.
- Contributors, W. (2020). Amino acid. Wikipedia.
- Dresden, D. (2018). Lysine health benefits: Evidence and food sources. Medicalnewstoday.com.
- Frank, K., Patel, K., Lopez, G., & Willis, B. (2019). Whey Protein Research Analysis. Examine.com.
- Halton, T., & Hu, F. (2004). The effects of high protein diets on thermogenesis, satiety and weight loss: a critical review. – PubMed – NCBI. Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Lawler, M. (2020). What Is Protein? How Much You Need, Benefits, Sources, More | Everyday Health. EverydayHealth.com.
- Leidy, H., Tang, M., Armstrong, C., Martin, C., & Campbell, W. (2011). The effects of consuming frequent, higher protein meals on appetite and satiety during weight loss in overweight/obese men. Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Leonard, J. (2018).Health benefits of protein powder. Medicalnewstoday.com.
- Martinez, K. (2020). Macro Calculations: Easy Way to Lose Weight – Supps Advisor. Supps Advisor.
- Nagdeve, M. (2020). 12 Surprising Benefits of Proteins | Organic Facts. Organic Facts.
- Paddon-Jones, D., Short, K., Campbell, W., Volpi, E., & Wolfe, R. (2008). Role of dietary protein in the sarcopenia of aging. – PubMed – NCBI . Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- Staff, G. (2020). 100% Grass-Fed Beef | Buy Healthy Meats Online | US Wellness Meats . Grasslandbeef.com.
- Weigle, D., Breen, P., Matthys, C., Callahan, H., Meeuws, K., Burden, V., & Purnell, J. (2005). A high-protein diet induces sustained reductions in appetite, ad libitum caloric intake, and body weight despite compensatory changes in diurnal pl… – PubMed – NCBI . Ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.

Alex is a former Personal Trainer and the go-to guy when it comes to his blog - SuppsAdvisor.com. Every piece of content is thoroughly checked, rechecked, and then published by Alex!
He is very much into sports activities such as tennis, skiing, surfing and of course working out.
His motto: be active, healthy, and happy!


