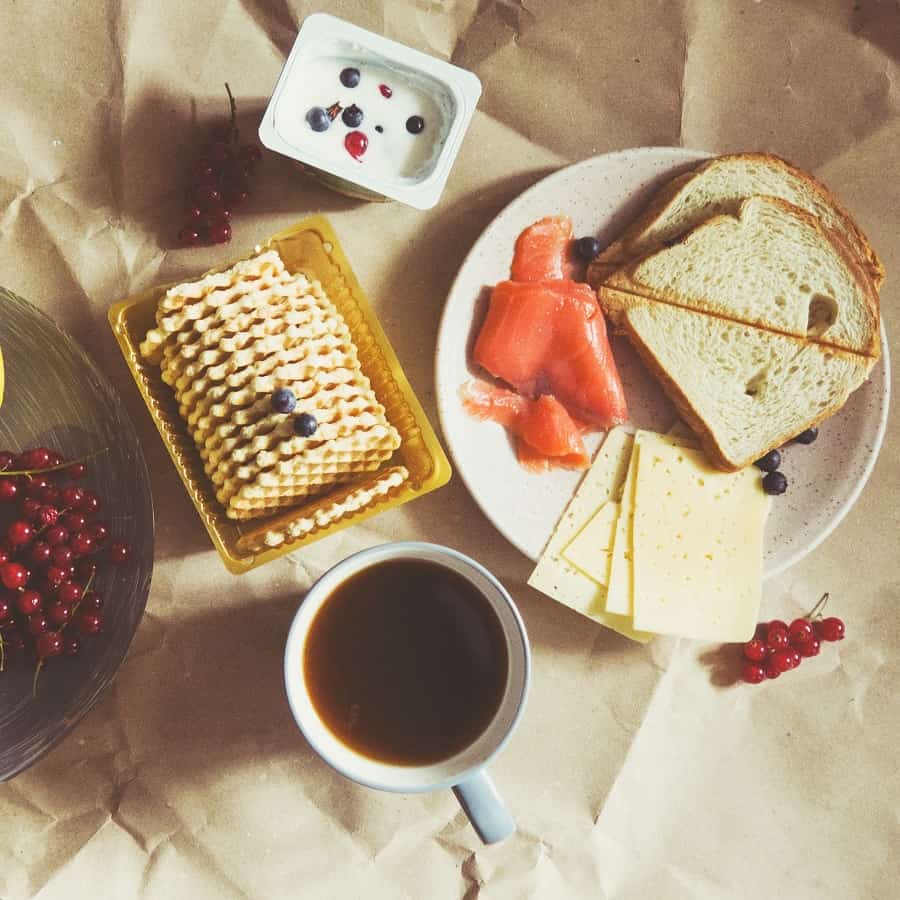
If you’re like me, you want to put only the highest-quality products into your body.…
TOC
Pre-Workout Nutrition: What Food Should I Eat Before a Workout?

01/25/2020 · 10 min reading
While working as a personal trainer, I had a client that wasn’t seeing the results that she wanted. She was experiencing fatigue during workouts, as well.
My first question for her was, “What have you been eating before coming here to train?”
Her reply explained what the problem was. My client was eating junk food before training. She was eating things such as donuts combined with very sweetened coffee. There were no components of a healthy meal before training.
Pre workout nutrition is crucial to maximizing your workout performance and physical progression.
A Few Words About What We Eat
Many people underestimate the value of pre workout nutrition and the impact it makes. Nutritious foods fuel your body and ramp up your body for the highest performance. People tend to believe that only their diet during the rest of their day matters. Your pre workout meal sets the stage for how your body will react during your workout.
One of the most recommended ways to judge your nutrition is to go by macronutrients. These three macronutrients are carbs, protein, and fat. Without these compounds, your body will not have the energy you need to function.
Consuming adequate amounts of each macronutrient makes your body operate in tip-top shape. Each macronutrient has its benefits, and you can combine them or ingest them on their own. Here is a little bit of a breakdown of each macronutrient and its role in your body.

Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary macronutrient that provides your body with energy. Carbs are the most necessary macronutrient for optimum nutrition pre workout. They supply your body with 45-65% of your energy.
Carbs convert into glucose, which then enters cells and further converts to ATP. ATP, or Adenosine Tri-Phosphate, provides energy for physical actions such as muscle contractions.
Excess glucose turns into glycogen, which gets stored in the liver and muscles for later use. Glycogen stored in muscle cells provides backup energy for endurance or high-intensity training. It is not uncommon for athletes to carb load by eating a high-carb diet for several days in a row. This process allows them to store even more energy for ongoing rigorous training.
Non-digestible carbohydrates don’t contribute to the cellular energy process. Instead, these carbohydrates act as dietary fiber. These carbohydrate sources include fruits and vegetables. There are also simple and complex carbs. Simple carbs break down in your body faster and are ready for use sooner. Complex carbs take longer to digest and metabolize.
No matter which type of carbohydrates you consume, 1 gram is equal to 4 calories.

Protein
A pre workout meal that’s high in protein has shown to optimize performance. Additionally, protein accelerates muscle protein synthesis. This synthesis process is part of the anabolic reaction that helps build up your muscle mass. Protein synthesis also aids muscle recovery.
The more muscle mass you gain, the more strength and muscle performance you have. Examples include whey protein, meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, beans, and nuts.
Protein is a vital building block to life, and 20-35% of your diet should consist of protein. One gram of protein supplies four calories.

Fats
Hearing that fat is part of your necessary macronutrients may make you cringe and want to run. Fear not, there is a distinction between types of fats. Adding healthy fat into your diet allows you to store backup energy and crucial vitamins. These vitamins include A, D, E, and K vitamins.
Most people need approximately 10-35% of their food intake to be healthy fats. Fats have three different forms, which include saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats.
-Saturated fats come from meats, dairy products, and other animal-based items. You should consume small amounts of these fats and not overdo it.
-Unsaturated fats come from plant-based sources such as oils, nuts, and avocados. Unsaturated fats are the healthiest and should make up most of your fat intake.
-Trans fat comes from sources such as fast food and junk food. Trans fat raises your cholesterol levels and puts you at a higher risk of heart disease.
Trans fats are the fat sources that you should avoid whenever possible. These fats, when consumed in excess, can cause heart and coronary diseases.
Fats provide the highest amount of calories, clocking in at nine calories per gram.
Best Time to Eat Before Workout
To get optimum nutrition pre workout, timing your meal can make a difference.
The macronutrients that you need in your pre-workout meal depends on when you are eating. Another critical factor is the duration and intensity of your workout. Combining protein and carbs is a recommended place to start, no matter what the timing is.
1 Hour Before
Sometimes, eating a few hours before a workout isn’t possible. Although eating less than an hour before your training isn’t ideal, doing so now and then is okay. If you are eating so soon before your workout, you should eat foods that are easy to digest.
You should avoid fats in this situation, so your stomach doesn’t get upset. Examples of ideal foods include fruits, yogurt, and protein or nutrition bars.

2 Hours Before
This timing provides the opportunity to incorporate all three components of your macronutrients. Your primary focus is consuming plenty of protein and carbs to fuel your body and muscles.
Example foods include protein shakes, whole-grain cereal, fruits, oatmeal, almonds, and milk.
2-3+ Hours Before
If you are consuming your meal three or more hours before, it allows you to eat heavier foods. The reason is that they will have more time to digest. For optimal nutrition pre workout, a meal within this time frame is ideal. You can include more healthy fats, carbohydrates, and protein-rich foods.
Examples include whole-grain bread, eggs, lean meats, avocado, fruits, vegetables, and brown rice.

Pre Workout Supplements and Ingredients That May Improve Your Performance
Pre-workout supplements are supplements that intend to improve your performance and energize you. Consistency between different brands and formulas is sparse. Still, there are a few common ingredients that offer specific benefits and options.
Multi-Ingredient Pre-Workout Supplements
Many gym-goers prefer to get many benefits while only having to take a singular dose. Multi-ingredient supplements combine several beneficial compounds for significant results. These results are significant and achieved without taking these supplements one by one. The most used ingredients in these are creatine, caffeine, amino acids, and B-vitamins.
Creatine
Creatine is a natural chemical that assists in increasing energy and improving strength. Research dictates that creatine helps speed up recovery and build your muscles. Furthermore, creatine can promote adaptation to high-intensity exercise and optimize performance. Creatine is available in multi-ingredient supplements or as a supplement of its own. Usually, these supplements come in powder forms that you mix with water and drink.
Caffeine
The beloved ingredient in coffee, sodas, and energy drinks exist in many supplements. Caffeine increases your focus. Additionally, caffeine makes your brain and body more alert and improves performance. Btw, on the go, here is a good selection of specialty instant coffees that you definitely will enjoy.
Taurine
Taurine is a unique amino acid that doesn’t play a role in protein synthesis. Even so, taurine shows benefits for exercise performance. Benefits include fat burning, muscle cell protection, decreased fatigue, and improved muscle performance.
Nitric Oxide Precursors
Nitric oxide is a natural compound that your body produces, which improves blood flow. Nitric oxide precursors include L-arginine, L-citrulline, and dietary nitrates. The intended purpose is to enhance the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to muscles. Nitric oxide precursors often appear in pre-workout supplements to improve performance.

Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs)
Branched-chain amino acids consist of 3 essential amino acids. Those amino acids are leucine, isoleucine, and valine. These specific amino acids are part of a group of amino acids called “essential.” This term means that they come from your diet. BCAAs have a host of proven benefits for exercise.
These benefits include amping up protein synthesis and reducing muscle soreness. They decrease exercise-induced fatigue, prevent muscle wasting, and benefit patients with liver disease.
Beta-Alanine
Another amino acid that you may find in pre-workout supplements is beta-alanine. This amino acid has proven that it increases endurance and reduces fatigue. Beta-alanine is especially useful for short bursts of intense training.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates in pre-workout supplements work the same as dietary carbohydrates. If you need to supplement your carbs or you are carb-loading, this extra ingredient is helpful. Again, carbohydrates energize the cells in your muscles so that they perform better.
Beetroot Juice
Beetroot juice is one of the nitric oxide precursors that I mentioned. The nitric oxide, combined with increased blood flow, improves endurance muscle growth.
B-Vitamins
B-vitamins are an excellent addition to pre-workout supplements. The combination of B-vitamins, caffeine, creatine, and amino acids show significant benefits.
The main benefits include reduced fatigue, increased endurance, and speeding up reaction times.

Natural Pre-Workout
Some people prefer not to take supplements. For some people, the idea of supplements may be off-putting. For others, the financial burden of supplements is too much.
In these cases, there are natural alternatives. For instance, caffeine can come from your cup of coffee. For a healthy and low-acid coffee try Lifeboost Coffee – great for sensitive stomach.
Simple carbohydrates exist in fruits such as bananas, grapes, and apples.
High-protein foods can substitute the amino acids found in supplements. These proteins include lean meats, dairy products, eggs, and nuts.
Beetroot juice is available to drink by itself without requiring multi-ingredient supplements.
For a wealth of B-vitamins, there are plenty of alternatives to eat before your workout. These foods include:
- Salmon and trout
- Leafy greens
- Liver
- Eggs
- Milk
- Beef and pork
- Oysters, clams, mussels
- Legumes
- Poultry
- Yogurt


What is Also Crucial
Your pre-workout nutrition can only do so much for you if you don’t care for your body in other crucial ways. These other necessities for your physical performance include hydration, sleep, and diet. Without this triad, your efforts will not prevail.
Hydration
Your physical makeup consists of 60% water. Water is an integral part of your body functioning as it should. How much of a difference does water make?
Water regulates your temperature, which happens through sweating during workouts. You risk the dangerous overheating of your body if you don’t have enough hydration to sweat.
Carbohydrates and protein need water to metabolize, which defeats your efforts.
Water is necessary for keeping your joints lubricated and preventing damage.
Also, adding sodium helps you keep fluids in your body for longer. This effect helps to prevent dehydration and keep your electrolytes balanced. Electrolyte imbalance can be hazardous, especially when you are sweating a lot.
Hydration is vital to enhance your performance and safety.
Sleep
Sleep creates a valuable loop. Getting the right amount of sleep keeps you alert and more energized. When you get a solid workout in, your body reactions trigger in such a way that promotes deep sleep. This cycle continues, benefitting your body and putting you at peak performance.
Diet
Incorporating nutrition-heavy foods into your pre-workout routine is invaluable. Even so, spending the rest of your day consuming junk and foods full of trans fats, your efforts will not pay off.
Maintaining a clean diet is imperative to progression. Everyone rewards themselves with unhealthy foods at some point, but moderation is key.
Safety and Quality
One huge factor in safety and quality is the lack of regulations. Supplements may make false promises, mislead you, or contain banned substances without warning. There is no actual proof of the safety and quality of different supplements.
Some supplements do provide proof through certification organizations. Organizations include the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the United States Pharmacopeia (USP).
What have you been eating before coming here to train?
Conclusions
When making a significant improvement in your physical performance, pre-workout nutrition is essential. Knowing what foods to consume and the best times is foundational knowledge. You should take care of your body at all times rather than only before your workout.
Chris Heria: A whole day of eating + workout
Join Chris Heria as he shows you what he eats for a whole day based on the shoulder workout he has planned. Use these workouts and fitness nutrition tips for real results!!!

Alex is a former Personal Trainer and the go-to guy when it comes to his blog - SuppsAdvisor.com. Every piece of content is thoroughly checked, rechecked, and then published by Alex!
He is very much into sports activities such as tennis, skiing, surfing and of course working out.
His motto: be active, healthy, and happy!
